Forklift Engines: Types and WorkingReading time: 07 min 00 sec. Table of Contents1. Forklift Engine2. What are the types of Forklift Engines? 3. How does a Forklift Engine work? 4. What does a Forklift Engine do? 5. Why choose Lift Part Warehouse to buy Forklift Parts? 6. Takeaways Forklift EngineA forklift engine refers to the engine installed in a forklift or any similar powered industrial truck. Forklifts are vehicles used in
Forklifts were designed for lifting goods with their forks. The primary purpose of these forklifts is to keep up with automation needs. The development of Forklifts started when cars were developed, which made it necessary for materials handling equipment to develop too to increase picking efficiency through mechanical means. The manufacturer and model of forklift trucks are powered by
Most modern classes have safe working loads that range from 2,000 to 4,000 pounds. Forklifts can be electric, powered by batteries, compressed air, or fossil-fueled. Forklift engines are also known as forklift motors, and these could either be in the form of internal combustion (IC), electrical, or even pneumatic motors.
Forklifts were initially used to move goods manually, and then later, automated mechanical means were developed for this purpose. Forklift engines became indispensable in the 20th century when building construction increased, and materials handling equipment became necessary due to automation needs.  What are the types of Forklift Engines?The Forklift Engine is generally classified into 5 categories: Internal combustion (IC), electrical, hydraulic fluid power motor (employing oil pressure via a hydraulic pump), Pneumatic motors, and finally, Scissor lift Forklifts. These engines come in two types:
Forklifts are either powered by batteries or by internal combustion engines. Forklifts can lift items off the ground vertically or elevate them at different angles. Forklift truck is widely used in
The world has now started focusing on sustainable development, including reducing greenhouse emissions by recycling waste materials. This engine runs on fossil fuels that emit greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, increasing global warming problems. 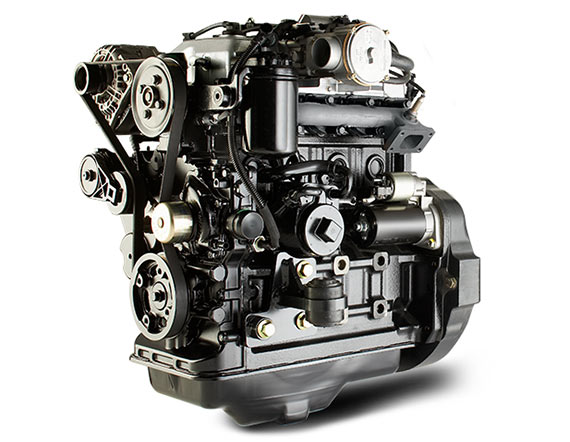 Internal Combustion Engines of ForkliftsForklift trucks have various IC engines: Some use two-stroke engines, and others four-stroke engines. Four-stroke engines are more common and generally work by drawing in a mixture of fuel and air;
Forcing the piston downwards, using the energy created to turn the gearbox, and then expelling exhaust gases as it reaches the top.
This happens four times for each revolution of the engine's rotor (hence, four-stroke), resulting in higher efficiency and less pollution. On the other hand, forklifts with diesel engines can run for longer between refuelings but need more careful servicing due to the fine tolerances of their fuel injection systems.  How does a Forklift Engine work?Forklift engines are very different from the engines found in cars. In a car, you can easily accelerate up to high speeds because of your engine's ability to produce power. Forklifts, however, need an engine that can provide strong torque at low speeds because turning a heavy load requires a slow start. These engines also have to be lightweight and compact because they will be located inside the forklift truck. These factors lead designers toward one type of engine – the internal combustion gasoline engine. Internal combustion means that petrol (gasoline) enters a chamber compressed and ignited by sparks created from an electrical current. It jumps gaps in a rotor within the chamber. This rapidly burning petrol creates a great deal of energy, used to power a rotor that turns a gearbox. The gearbox allows the engine to operate at a range of speeds. The higher the speed, the more energy is required, and thus the more petrol is used.
These engines achieve their torque by using large pistons to create small amounts of motion with each turn. To achieve this, they need to use low-octane petrol, which has less resistance than high-octane fuel. These engines also have very few cylinders – generally just two or four – so each piston only needs to move up and down a short distance and so spin quickly and generate lots of energy. Forklifts usually run on unleaded petrol, which is cheaper and safer than other petrol. 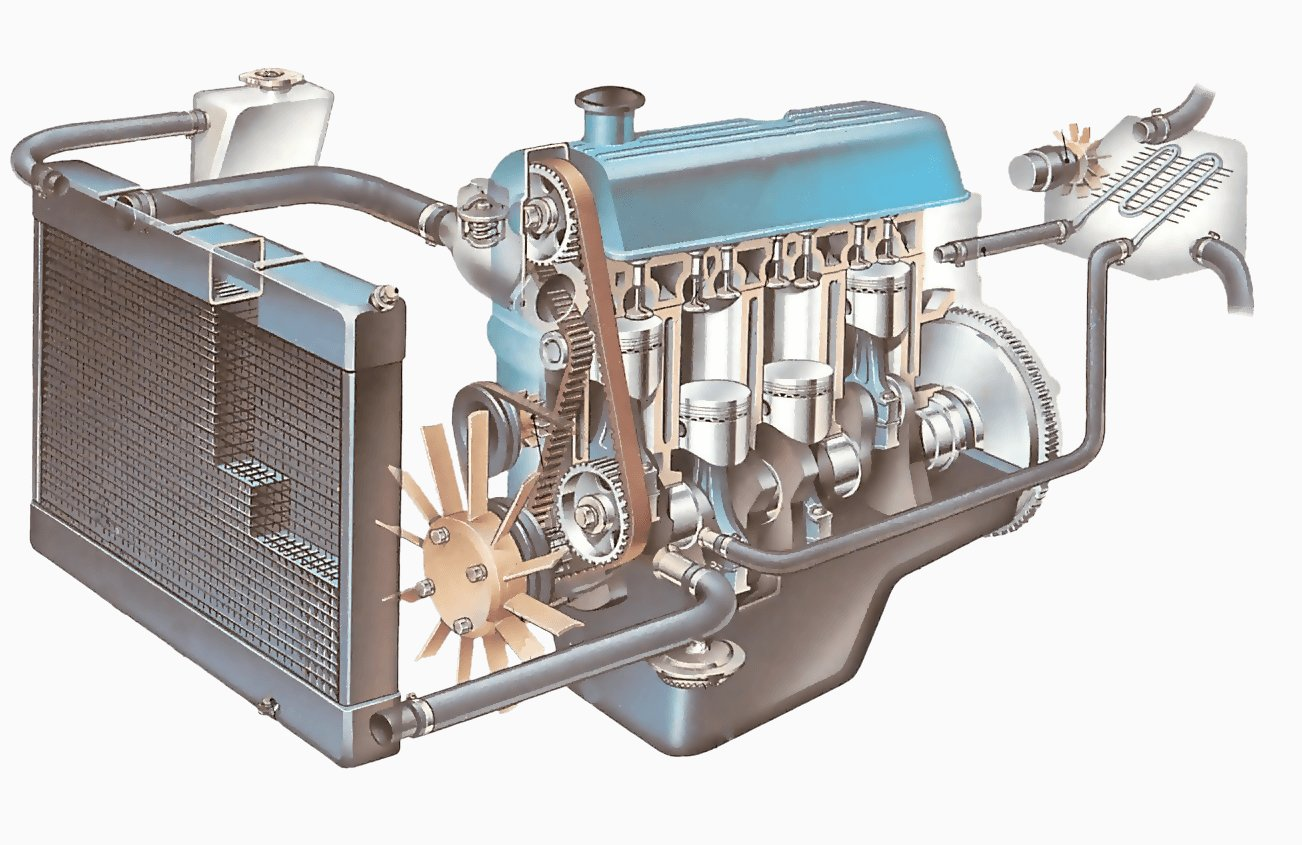 What does a Forklift Engine do?Forklifts are warehouse machines that are used to raise and lower goods. Forklifts have a range of tasks that require the use of different engines. Lift Parts Warehouse's engines are suited for many available Forklift uses. Forklifts come in smaller sizes, so it may be best to purchase an engine specially designed for small lift trucks. Larger Fork Lift Trucks that could transport more than 1,000 lbs should use engines ranging from 19-35 horsepower or more, depending on applications. The engine is responsible for powering the machine. Forklifts do not require fuel, although they function by using an internal combustion process with four cycles: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust. During the intake cycle, the piston moves down toward the crankshaft. These engines are designed to be durable and withstand their environment. Forklifts are used in rough conditions; therefore, they must handle jolts, bumps, and vibrations without causing harm to their payloads. Forklift manufacturers use heavy-duty materials like cast iron blocks with aluminum heads or fully machined bores that can very effectively dissipate heat while transferring energy into the rotational motion of the crankshaft. These engines typically operate at speeds between 2,000 rpm and 3,500 rpm, with lower-end models working at 2,700 rpm (depending on torque output). Each engine is attached to a drive coupling via a flywheel, and a torque converter locks the engine to the transmission's input shaft. Hydraulic pumps driven by the crankshaft activate forklift transmissions. Forklift transmissions use a series of gears to create as many as 20 different forward speeds with two reverse speeds. Forklifts typically have a top speed of around 15 mph with a range of 4-6 miles operating on one gallon of fuel, depending on terrain and load weight/size.
Forklift engines need to be inspected regularly before being put into service. The first thing that should be checked is any leaks within the system, especially in hydraulic systems where oil may drip or seep from hoses or seals. Secondly, loose items should be removed from the engine. Loose items like bolts, screws, or any other foreign objects could cause damage to the engine upon startup. These engines may last for thousands of hours (operating time), but they need regular inspections and maintenance to operate at peak performance levels. Why choose Lift Parts Warehouse to buy Forklift Engines and their Parts?What if I told you that buying Forklift Engines doesn't have to struggle? That's right, Engines (and other replacement parts) don't have to be hard to find or expensive. Forklifts are complex machines, and it makes sense that the part required for proper operation may not always be available at traditional retailers. Forklift operators who demand quality from their equipment turn to Lift Parts Warehouse when they need new Forklift Engines. Takeaways
|

First Order Special
GET 5% OFF
On Your First Purchase!
Use this discount code
5PERCENTOFF
note: One redemption per account/IP address only

